什么是尾递归
尾递归是指递归调用作为函数执行的最后一条语句,这样的情况下递归调用发生时,当前的栈帧就不需要了。如果语言有对尾递归做这样的优化,那么不论尾递归调用多少层,都不会有栈溢出的风险。特别注意的是,类似于下面这样的代码不是尾递归的,因为它执行的最后一条语句是 h + sum_result 而不是 sum(t) ,换句话说,这里调用 sum 时,栈帧还不能抛弃,因为栈帧中还需要保存 h 。
更详细的介绍请看: https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E5%B0%BE%E8%B0%83%E7%94%A8
|
|
非尾递归的实现
|
|
以上代码以一种最容易想到的方法实现了 foldRight, 但是很遗憾,它不是尾递归。::方法是常量时间完成,不涉及递归,后面不再解释。递归调用 foldRight 返回后还需要使用 h 和递归结果作为参数调用 op,栈帧中还需要保存 h 和 op,所以以上实现不是尾递归的。
尾递归的实现
虽然直接实现 foldRight 的尾递归版本有困难,但是 foldLeft 却很容易用尾递归实现。那我们实现一个尾递归的foldLeft,然后翻转 list 调用 foldLeft ,以此来实现 foldRight ,这样可行吗?下面试试看。
尾递归的 foldLeft
|
|
以上实现,最后执行的代码就是对foldLeft的递归调用,栈帧中需要保存任何信息,显然是尾递归的。
使用 foldLeft 实现 foldRight
|
|
这样就完了吗?当然没有,上面的实现使用了reverse函数,得尾递归实现reverse才行
尾递归实现reverse
这里就不卖关子了,直接使用 foldLeft 来实现 reverse 就可以了。
结果检验
上面有了 foldRight2 和 foldRight 两个实现。我们用一个长 list 来分别调用两个函数看看是否栈溢出。
上面使用了一个长度为10000的 list,计算所有元素的和。
使用 foldRight2 时发生了栈溢出,根据jvm启动参数的不同,发生栈溢出的临界值是不一样的。
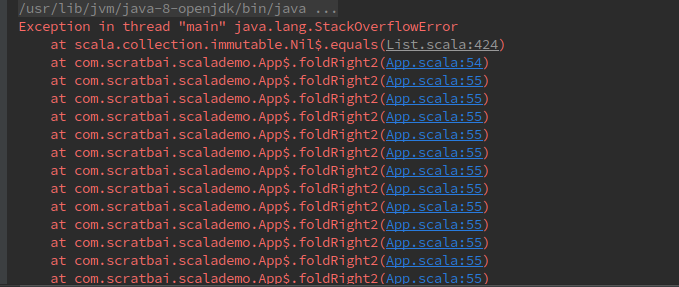
使用 foldRight 时正确输出了结果
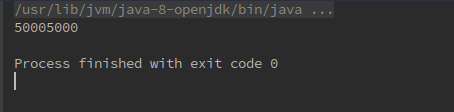
说明这里的尾递归实现是正确的,并且Scala的做出了正确的优化。